Big Data Outcome 1
Topic 1-4
This blog will go over the first Outcome For The Big Data course which is 1 to 4 in the introductory page these topics will are
- definition of big data
- historical development of big data
- growth of data
- reasons for the growth of data
1.Definition of big data is the term used to describe a large amount of data which is beyond the human ability to traditionally process it with tool, Big data is used to analyse patterns, trends and relationships which is then used to analyse how someone might behave either on the internet or from information that has been gathered like if the person went to jail and the likely hood that they might reoffend. Big data is classed as three main data sets these being Structured Data, Semi-Structured data and Unstructured data
Structured data
Structure data is a classification of data which can stick to a already existing data model which makes Structure data the easiest of all the classifications to analyse. Structured data adjusts to a table data set with its rows and columns which can be used by app like excel or SQL databases.
Unstructured data
Unstructured data is data which doesn't conform to traditional data models or sets. Unstructured data is usually text heavy but can include data sets which has dates, numbers or facts. this causes data sets to have a lot of irregularities and ambiguities when looking at them which is why its called unstructured data.
Semi-structured
semi structure data is a data set which does not conform to the usual structured or unstructured data sets but contain tags or other markers to help separate elements and enforce hierarchies . Examples of semi-structured data include JSON and XML files which are both semi-structured data sets. Semi-structure data exists because it is a easy middle ground between the structured data and the hard to read unstructured data.
2.The term Big data has been used the 1990's. Big data has been used through out the centuries to try and analyse possible trends or decisions. Its important to realise the techniques which where used and evolved into the modern day techniques that current big data analysts use, until the 1950's 90% of data analysis was manually done and written on paper, After the 1950's data analysis was slowly swapped to computers compiling mass data sets which computers could analyse terabytes of data in seconds, as the internet grew the amount of data grew as well, The total amount of data has grown past human comprehension as the total amount of data generated in 2013 was 4.4 zettabytes and has ten times since 2020 going from 4.4 to 44 zettabytes.
3. The growth of data has increase exponentially since its inception in the 1990's. The growth of data can be split into three phases which conform to every step of the internets growth, Big data phase 1.0 was the first phase in the big data phases, where it relies heavily on storage, extraction and optimization techniques which are used commonly in relational database management systems, Big data phase 1.0 provides the foundation of which big data is used today as it uses techniques which would be common place in phase 3.0 such as database queries, online analytical processing and reporting tools. The second phase of big data, big data phase 2.0 started at roughly the 2000's as the growth of the internet and web started to show unique ways of data collection and analysis, Company's such as yahoo and amazon started to collect and analysis customer behaviour. HTTP web traffic introduced a massive increase of unconventional data forms such as semi-structured data and unstructured data sets. With these new datasets company's needed to find new ways and increase storage solutions to deal with these new data types. The current phase which big data is on is 3.0, with the advent of mobile devices mass adoption it gives company's more data to analyse along with the usual click and search data but also gives company's a new data set which is GPS location data, it gives company's the ability to track your movement physical behaviour and even health related data. with the advent of sensor based internet devices the data generation increases exponentially as internet of thing devices (IoT) like TV's, Smart assistants, thermostats and wearables collect zettabytes of information daily it means that company's have a new way to analyse data sets.
4.Reasons for the rapid growth of big data include the aggressive acquisition and permanent retention of data with data sets becoming so massive. Along with the growth of big data the cost to store all that data has decreased while the total amount of data which can be stored has increased, another reason for the growth of big data is the rapid increase of business analytics which the market for business analytics is higher than 100 billion dollars. Security is another reason for the rapid growth, as company's get bigger they harvest more security data which include audio, video surveillance and system data logs which can all be analysed by big data. The increase of Internet devices such as phones and tablets increases demand for data analytics, with the growth of the cloud it allows company's to store more data cheaper.
Topic 5-8
5.Value of data(including future value)
6.Traditional statistics(descriptive and inferential)
7.limitations of traditional data analysis
8.characteristics of big data analysis(including visualisations)
Value of data
The value of data describes the impact, insights or benefits which is gotten from analysing. The value of data measures how effectively data is used to drive business outcomes and help improve decision making and optimize processes. The value can be split into three sections Statistics, business and general. Statistic, the value of data is content which fills out a table space these could include numbers or words. In business, data values refer to the total measurable financial impact of how it applies to an organisation and in general it refers to the benefits and advantages that can be used from data these decisions include innovations, services and security
Traditional Statistics
There are two types of traditional statistics which are used in Big data these are Descriptive statistics and inferential statistics. Descriptive statistics describe data, descriptive give information which describes data in a very accurate manner, a complete information data set is provided Descriptive statistics might not be able to extended to another group. Inferential statistics Studies a sample of the same data. Inferential statistics can be extended to a similar large group and can be represented by a graph.
7.With the constant increase of data growth from new devices coming the requirement to analyse the data increases, traditional data analysis relies on structured data which is organized with specific methods such as surveys, questionnaires and other forms of data collection, as other forms of data such as unstructured can give more valuable data to businesses, traditional data analysis methods are also time consuming when dealing with tons of data, an example is a survey can take months to complete which then needs to be analysed. Limited accuracy is another issue which faces traditional data analysis as it can be prone to errors and inaccuracies
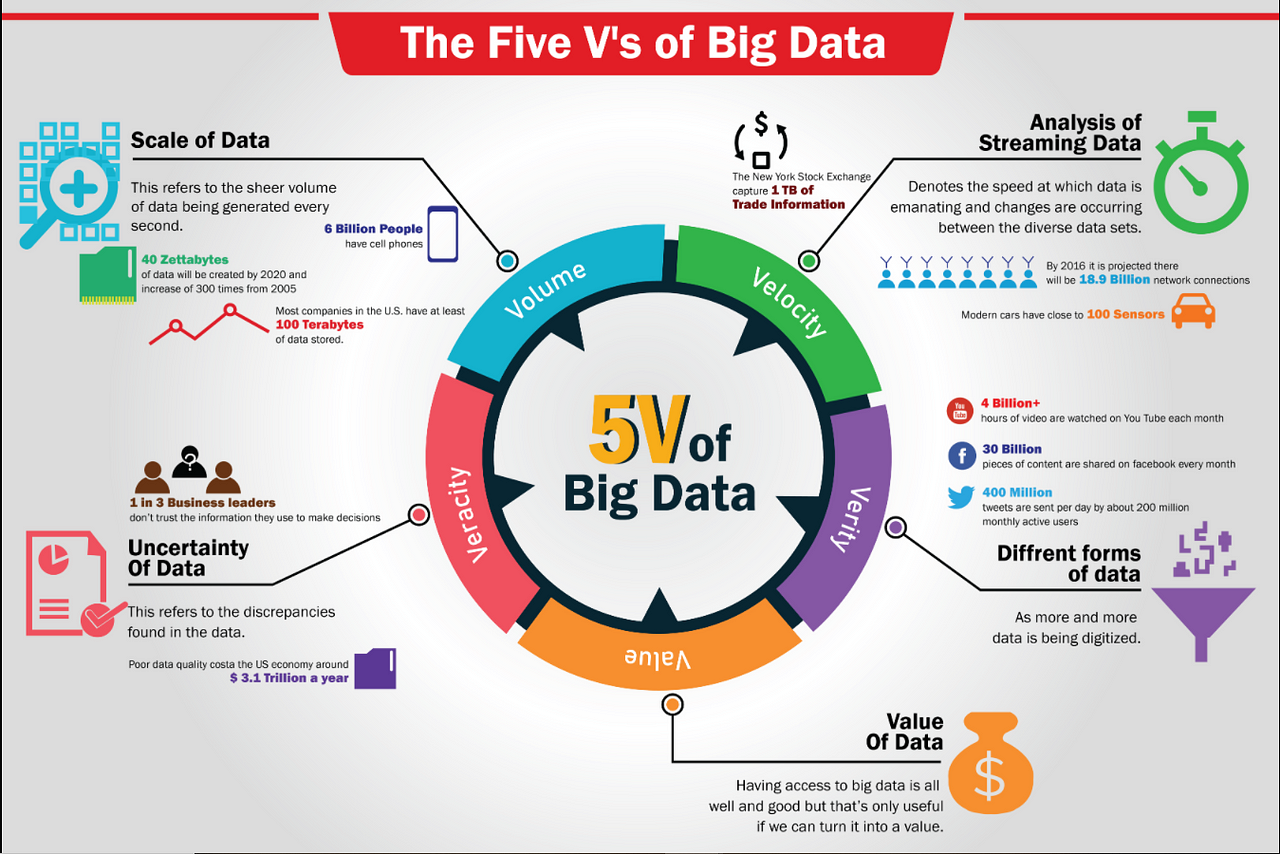
8.The value of data can be split into 5 V's these 5 V's are Volume, Velocity, Variety, Veracity and value each V describes a different characteristics used in big data, the first Big V is Volume, volume dictates the amount of data which exists, Its is the initial size and amount of data which is been collected and stored. The next Big V is Velocity, velocity is characterized on how quick that data is being generated So that business can make the best possible decision for their businesses,(add more if needed), The third V is variety, This refers to the diversity of data types which an organization would collect from different data sources these data sources might vary in value. The verity of data includes structured, unstructured and semi-structured data (more), the forth V is veracity, Veracity is the quality, accuracy, integrity and credibility of data which has been gather. Data could have missing pieces, be inaccurate or might not be able to show real insight, This is where veracity comes in where it shows the level of trust in collected data. The last V type is Value, Value refers to the benefit which can be gathered from all other of the 4 V's and big data which is provided and can be used.




Great breakdown of Big Data concepts! Your explanation of structured, semi-structured, and unstructured data is clear and insightful. Looking forward to more posts diving into how businesses and technology leverage these datasets!
ReplyDelete